Engine misfires that are not repaired promptly are the number one reason for damaged catalytic converters. A broken engine cylinder can damage the catalytic converter in a car, shortening its lifespan by several years. In some cases, it may even cause the converter to melt down completely.
What is a Catalytic Converter?
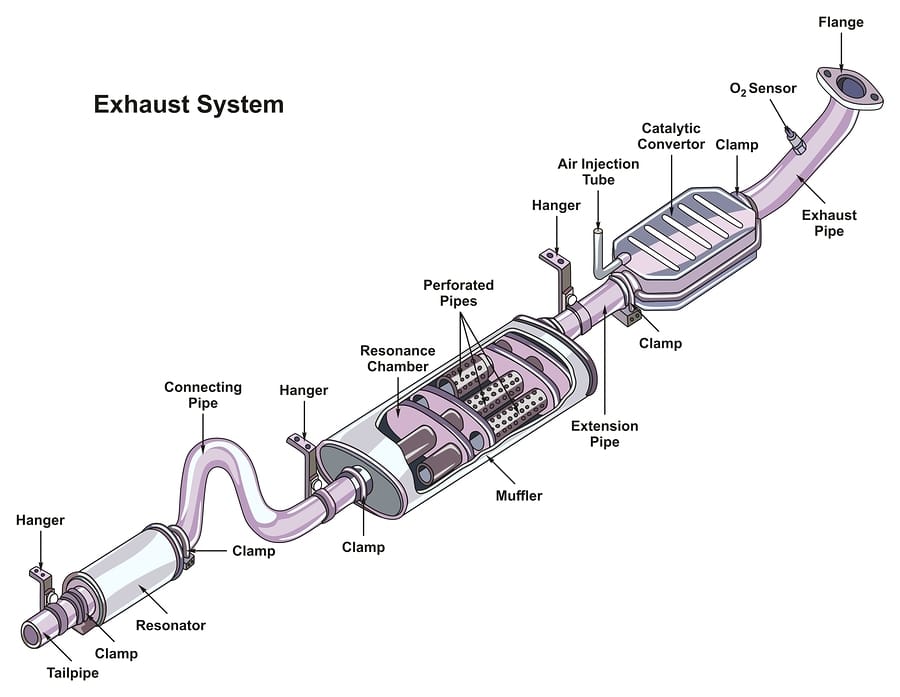
An emissions control device, known as a catalytic converter gets installed in the exhaust system of gasoline or diesel engines to control emissions. Its purpose is to reduce the emissions of harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons released into the environment through the vehicle’s exhaust.
The catalytic converter converts harmful pollutants into less toxic substances through a chemical reaction. Inside the catalytic converter are two types of catalysts: a reduction catalyst and an oxidation catalyst.
The reduction catalyst reduces the amount of nitrogen oxides in the exhaust, while the oxidation catalyst converts carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into water vapor and carbon dioxide.

In some ways, the vehicle’s catalytic converter performs in the same manner as the engine. The catalytic converter breaks up hydrocarbon molecules by oxidizing the hydrogen and carbon into H2O and CO2. The mixture in the converter initiates a chemical reaction when it contains around 50 parts per million of hydrocarbons at 1% O2, maintaining the reaction within the converter. This reaction generates enough heat to maintain the converter at ‘cooking’ temperature.
Causes of Catalytic Converter Damage
The unburned mixture is captured inside the catalytic converter because the oxygen and fuel are not ignited inside the cylinder during a misfire event. While the converter can cook these contents, the significantly higher oxygen levels and parts per million of hydrocarbon generate a level of heat energy output that is unmanageable by the converter’s ceramic substrate.

An engine misfire doesn’t always impact the converter. However, a fuel imbalance—either too little or too much in the cylinder—stops the converter’s mixture from igniting. Conversely, misfires caused by engine mechanical faults or ignition issues usually send a high concentration of hydrocarbons and O2 into the converter, potentially affecting its function.
Catalytic converters can be damaged by a variety of factors. Here are some common causes of catalytic converter damage:
- Age: Over time, catalytic converters can wear out and become less effective at converting pollutants. The typical lifespan of a catalytic converter is around 100,000 miles, although this can vary depending on the vehicle and driving conditions.
- Contamination: Catalytic converter contamination can occur due to various factors, including leaded gasoline, oil or coolant leaks, and engine misfires. Contamination can cause the catalyst material to become coated or damaged, reducing its effectiveness at converting pollutants.
- Physical Damage: Road debris, speed bumps, and other obstacles can physically damage catalytic converters. It can cause the honeycomb structure to become cracked or clogged, reducing the flow of exhaust gases and causing increased backpressure in the engine.
- Overheating: The catalytic converter can overheat due to engine misfires, fuel system problems, or exhaust system leaks. Overheating can cause the catalyst material to melt or break apart, rendering the converter ineffective.
- Fuel Quality: Poor-quality gasoline or diesel fuel can contain higher levels of sulfur or other contaminants that can damage the catalyst material in the catalytic converter over time.
- Improper Installation: Improper installation of the catalytic converter, such as using the wrong type or size of catalytic converter, can cause damage to the catalytic converter or lead to increased emissions.
Overall, it’s important to maintain and replace a damaged or faulty catalytic converter to ensure the vehicle is operating within legal emissions limits and reducing its impact on the environment. Regular vehicle maintenance, such as oil changes and tune-ups, can also help prevent damage to the catalytic converter.

