Electrical
Ignition
The ignition system produces the high voltage required to create an electric arc strong enough to jump the gap of the spark plug. This electric arc, or spark, ignites the air / fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. The ignition system is also responsible for providing the spark at the appropriate time during the compression stroke.
The ignition system converts the 12 volts (V) from the vehicle’s battery to over 20,000V. The high voltage is needed to push the electrical current across the spark plug to create the spark. The spark ignites the air fuel mixture. If the voltage is not high enough to push the current, no spark, or a weak spark occurs, causing a misfire.
Spark Plug
Spark plugs are an important part of the engine’s ignition system and are responsible for igniting the air/fuel mixture in the engine cylinders. Over time, spark plugs can become worn and covered in carbon. Replacing spark plugs at the recommended interval helps to keep the engine running smoothly and efficiently.
Electrical Signal Evaluation
To evaluate an electrical signal in real-time a professional grade computer-based lab scope is used by the team of professionals at Hollenshade’s. When the electronic scope is used in conjunction with other tools, such as a high-fidelity pressure transducer, evaluation of engine functions can be made without excessive disassembly of components.
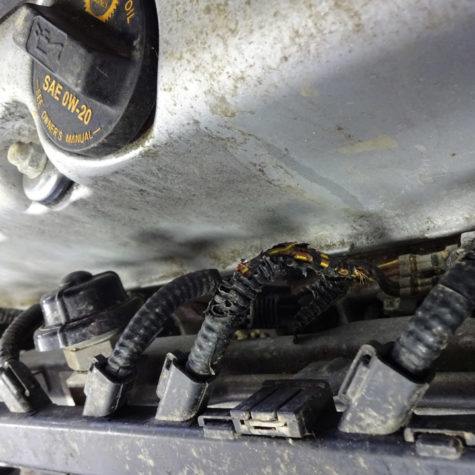
Electrical Circuit Diagnosis
Modern vehicles use computer modules to control the devices and systems responsible for proper operation. Monitoring and controlling the electrical circuits with computer modules allows for more advanced strategies such as Pulse Width Modulation.
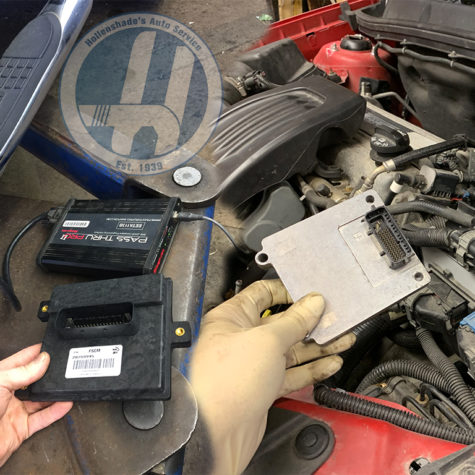
Computer Module Diagnosis
There are more and more computer modules contained in modern vehicles. These modules are located across the vehicle and are responsible for the control of both electrical signals and logic-based system operation.
Engine tuning
For an engine to operate efficiently, the air / fuel mixture must properly blend. Too much air and not enough fuel causes the mixture to be lean. Too much fuel and not enough air causes the mixture to be rich. Both cause the engine to not operate at its full potential. The ideal air to fuel ratio for gasoline engines is called the stoichiometric ratio. At this ratio of 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel, or 14.7:1, the oxygen and fuel consume completely, and the engine produces its maximum power.
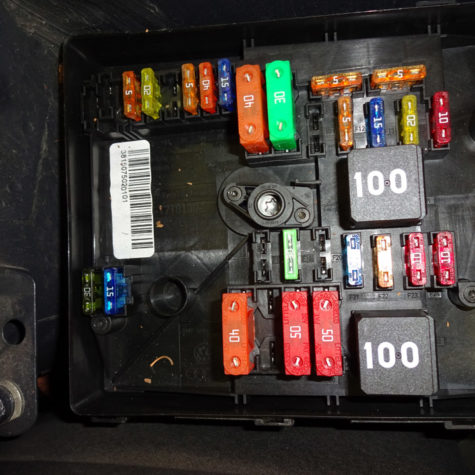
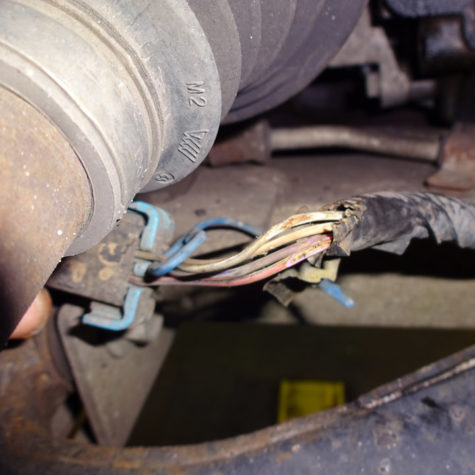
Electrical Load Diagnosis
Unwanted draws and/or drains on the vehicle’s electrical system can impact component function and performance. A professional technician, such as those at Hollenshade’s in Towson, can accurately pinpoint the source of a improper electrical load on one or more of the vehicle’s systems.